

Large-scale production processes are required before clinical trials can be carried out. However, they note that at present, the antithrombin variant can only be produced on a small scale. "These results clearly demonstrate that AT-N135Q-Pro394 can reverse the anticoagulant activity of fondaparinux and thus could be used as an antidote for this drug ," write the researchers in the journal Blood. For heparin overdose and is used to neutralize heparin during. Protamine sulfate works by binding with the heparin to inactivate its blood-thinning effect. This antidote (23 kD, 3-nm radius) was functionalized with 20 cationic binding groups for multivalent interactions with heparin and was. The researchers observed a similar antidote effect in vivo, as administration of AT-N135Q-Pro394 to mice treated with fondaparinux at five times the curative dose neutralized 86% of the anti-Xa activity within 5 minutes. Risk factors for these events include high doses or overdose. The standard treatment for heparin overdose is protamine sulfate. Recently, a cationic, dendritic polyglycerolbased heparin-reversal agent was shown to neutralize the activity of all clinically approved heparins in rodents (3 mg/kg, 5 min after heparin administration). In additon, AT-N135Q-Pro394 decreased UFH and LMWH anticoagulant activity by 76% in overdosed plasma, indicating that it acts as a potent antidote to all heparin-like anticoagulants. Moreover, the antidote effect was dose-dependant. They found that AT-N135Q-Pro394, at a concentration equal to the endogenous plasma antithrombin concentration, significantly reduced the fondaparinux concentration from 3.0 to 1.23 mg/l - a concentration equivalent to that used for curative treatment. An excess of protamine can contribute to coagulopathy, hence predisposing to bleeding with associated morbidity and mortality.To test the antidote's ability to reverse fondaparinux overdose, they added increasing concentrations of AT-N135Q-Pro394 to plasma spiked with approximately three times the maximal curative dose of fondaparinux. In some embodiments, the polymer of formula (I) or pharmaceutical composition according to the invention is for the treatment of a heparin overdose or for the. Antidote Protamine sulfate 1-1.5 mg, IV, for every 100 units heparin subcutaneous within 30 min of overdose, 0.5-0.75 mg for every 100 units heparin subcutaneous if within 30-60 min of overdose, 0.25-0.375 mg for every 100 units heparin subcutaneous if 2 hr have elapsed since overdose, 25-50 mg if heparin was given by IV infusion. What happens if you give too much protamine?īackground and objective: Protamine is routinely administered following cardiopulmonary bypass in order to neutralize the effects of heparin. “It binds to heparin to form a stable ion pair which does not have anticoagulant activity on its own, protamine has a weak anticoagulant effect.” Protamine sulfate is a drug that reverses the anticoagulant effects of heparin by binding to it. 2 hr: 0.25-0.375 mg/100 units of heparin.įlumazenil injection is indicated for a complete or partial reversal of the sedative effects of benzodiazepines in conscious sedation and general anesthesia in adult and pediatric populations.

How do you reverse heparin infusion with protamine?ĭose of protamine (mg) to neutralize 100 units of heparin
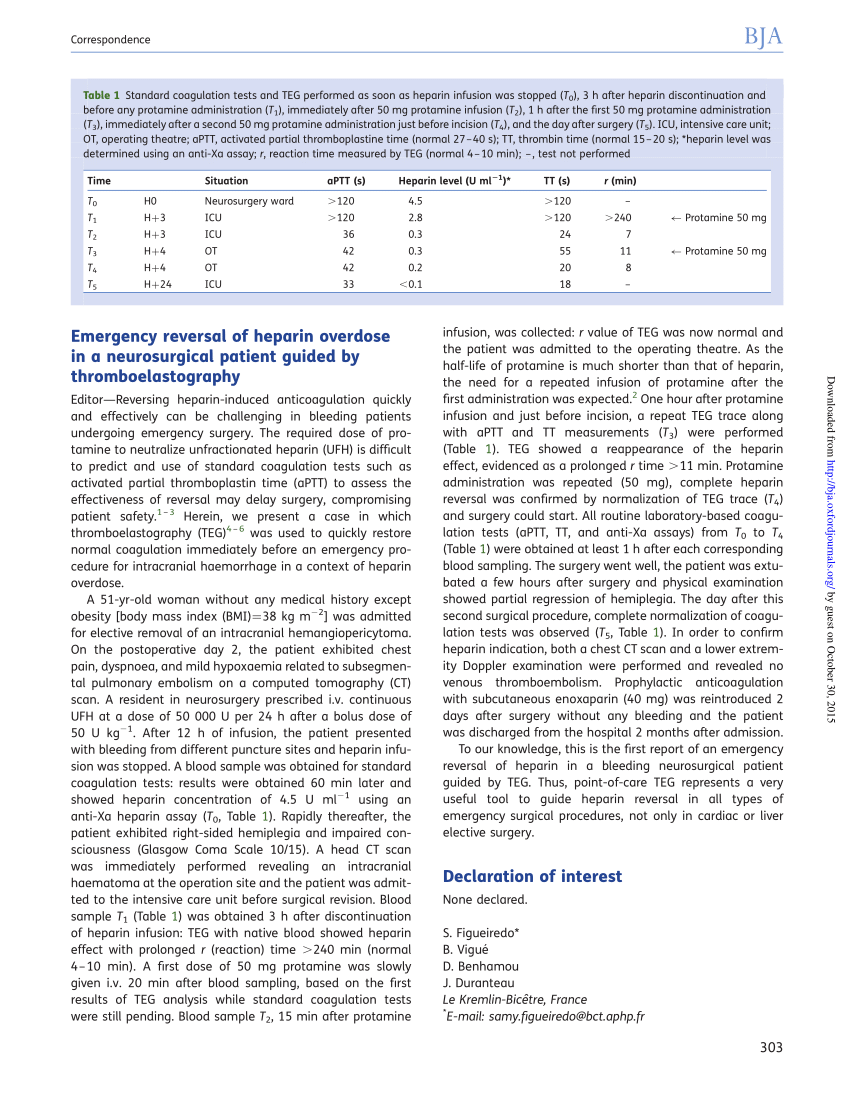
#Antidote for heparin overdose series
Keywords: glipizide, hypoglycaemia, lactic acidosis, metformin, overdose This is the first in a series of cases presented by the Western Australian Toxicology Service. Metfonnin overdose rarely causes problems. All results Study sets Textbooks Questions Users Classes. No more than 50mg of protamine sulfate should be given in any one dose. Sulphonylurea overdose invariably results in profound hypoglycaemia that requires resuscitation with IV dextrose and the use of octreotide as an antidote. Choose from 120 different sets of antidote for heparin overdose flashcards on Quizlet. Protamine sulfate should be administered by slow intravenous injection over a period of about 10 minutes. Treatment 1 mg for each 100-unit heparin, 1/2 dose if 3060 min 1/4 dose if 2 hr after heparin bolus 2550 mg slow IV over 15 min. No more than 50mg of protamine sulfate should be given in any one dose. Adults: Protamine sulfate should be administered by slow intravenous injection over a period of about 10 minutes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
